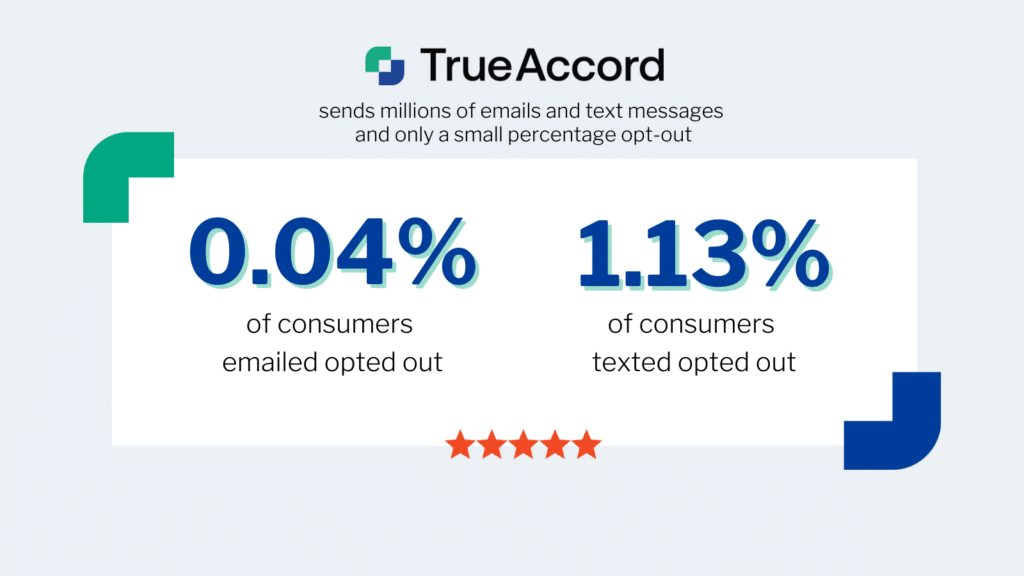
Today’s current economic climate is already influencing consumer spending and credit in 2024, and is becoming a hot topic for businesses seeking to engage past-due customers.
Economic Growth in 2023, But Slowdown Expected in 2024
Last year proved that the US consumer has been very resilient to the rumblings of a potential recession and continued to spend with surprising growth all the way through the end of 2023.
Despite inflation and high interest rates, consumers helped the economy end the year in a far better position than most predicted.
And consumers reported an uptick in optimism about the financial state, according to Deloitte’s ConsumerSignals financial well-being index, which captures changes in how consumers are feeling about their present-day financial health and future financial security based on the consumer’s own financial experience. We saw an increase to 101.4 in November 2023, up from 97.6 a year ago. Additionally, WalletHub’s Economic Index, which measures consumer satisfaction, rose by about 4% between January 2023 and January 2024.
But even as economic experts adjusted their outlook towards a soft landing and consumers reported a more positive financial outlook, 2024 is still expecting a slow down in consumer spending.
“Growing debt balances, stubborn interest rates and elevated prices are still a thorn for consumers, and contribute to their overall financial stability,” explains TrueAccord CEO Mark Ravanesi in his Q4 Industry Insights: Cautious Optimism with a Side of Holiday Hangover. “For lenders, service providers and debt collectors, guaranteeing repayment will still be a challenge [in] 2024.”
As Consumer Delinquency Rises, So Does Consumer Confusion
That financial holiday hangover Ravanesi described is a harsh reality for consumers: approximately one-third of American adults go into debt to pay for holiday expenses, contributing to their overall financial stability year-round. Credit card balances hit a trillion dollars in 2023, but that unprecedented milestone proved to just be another number as credit card balances continue to grow—by the fourth quarter balances increased to $1.13 trillion and the share of those balances that were at least 90 days delinquent approached 10%, an increase of more than two percentage points in a year.
In January, overall delinquency grew with a 2.31% increase in delinquent accounts and 10.49% in delinquent balances month-over-month. Today, about 61% of American households have credit card debt and the average credit card debt balance sits at $5,875.
Bottom line: households took on more debt at the end of last year and we’re seeing loans increasingly going bad, according to data from the Federal Reserve Bank of New York, leading to a shift in consumer spending for 2024.
On top of historic credit card balances, delinquencies continue to climb across the board: automotive, mortgage, bank cards, and unsecured personal loans.
The rising popularity of the Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL) options and their corresponding delinquencies are also a piece of the puzzle, but one that is not currently captured by the Bureau of Economics and falls into a category known as “phantom debt.”
“Today’s consumer is using more and different financial products,” shares Ravanesi. “Buy Now, Pay Later was a big driver of purchasing power [in 2023] amidst elevated interest rates. While a helpful product for consumers, BNPL can be tricky as it doesn’t show up on most credit reports and can be an invisible and unaccounted-for debt burden.”
With so many different BNPLs offered, consumers can be borrowing from a variety of different lenders all at the same time and it is becoming more difficult for them to keep track of the different payments—and easily slip into delinquency. This confusion can be especially detrimental considering consumers using BNPL as more likely to be “financially fragile,” as reported by the NY Fed, having credit scores below 620, being delinquent on a loan, or having been rejected for a credit application over the past year.
“It’s becoming more and more confusing for consumers,” TrueAccord founder Ohad Samet explained in a recent webinar. “And we’re seeing consumers often need help to organize the different debts.”
And then we add student loans back into consumers’ repayment mix…
The Impact of Resumed Student Loan Repayments
Millions of people are resuming another financial obligation every month: their student loan payments. This introduces one of the defining questions of 2024 for lenders and debt collectors:
How will student loans be prioritized among other payments and debts?
It’s a legitimate concern considering surveys found 45% of respondents used the student loan forbearance period to tackle other debts, including paying down mortgage/rent expenses (27%), credit cards (26%) and other past-due bills (24%)—and even before forbearance was lifted, 85% of borrowers already anticipated facing financial hardship due to student loan repayment, with 49% saying they’ll have a hard time paying other bills. In fact, 28% of student loan borrowers say the resumption of federal student loan payments will likely require them to take on new debt to manage their personal finances.
Only time will tell, but so far student loan repayment rates have been low amongst the 22 million Americans affected—in the first month of resumed payments, 8.8 million borrowers missed their student loan payment, equating to 40% of loan holders.
Whether they missed that first payment or not, student loan repayments resuming again are having a significant impact for those who borrowed—91% say financial stress is impacting their mental, physical wellness and student loan debt is a key driver of this financial stress.
So how can lenders and collectors effectively recover debts in 2024 given the rising delinquencies and rising financial stress for consumers?
Right Message, Right Channel, Right Time for Better Consumer Engagement and Debt Recovery
Consumers have more stress and demands on their attention than ever before so it should make clear sense that consumer experience is critical for an organization’s reputation, long-term success with customers, and how effectively you can collect even in late-stage delinquency.
Research shows that contacting first through a customer’s preferred channel can lead to a more than 10% increase in payments and that 14% of bill-payers prioritize payments to billers that offer lower-friction payment experiences. Plus, 71% of consumers expect personalized experiences, which means one-size-fits-all outreach isn’t going to cut it in collections. Your business must be able to engage with the right message, the right channel, and the right time to recover the most funds possible.
“If there’s one thing we’ve learned from our consumer interactions, including the 16.5 million we added in 2023, it’s that no two consumers are the same, and what works for one may not work for the next,” explains Ravanesi. “That’s why options are so important—in communication channel, customer support method, and perhaps most importantly, in repayment.”
Personalization of the collections experience—from channel to time of day to specific message—is critical in cutting through the noise and driving engagement and commitment, especially in today’s increasingly digital world.
“Digital is deeply, deeply ingrained in every group of the population,” Samet observes.
And consumers are engaging on more digital channels than ever before:
- 65% of American consumers have paid a bill by mobile device in the past twelve months
- 54% have used an online portal supplied by a biller
- 85% of consumers are already using digital bill pay
- 41% of consumers cite ease and convenience and 23% cite faster and instant payments as the most important reason to choose a digital channel
- 59% of consumers stating email as their first preference for debt collection, according to a FICO survey (versus only 16% want to receive a phone call)
Research from McKinsey concludes that consumers who digitally self-serve resolve their debts at higher rates, are significantly more likely to pay in full, and report higher levels of customer satisfaction than consumers who pay via a collection call.
Providing multiple repayment options, communicating through a variety of channels, reaching out at the optimal time of day, delivering the message in a way that best resonates with the consumer—all of these factors play a role in how effective your debt recovery strategy will be.
The TrueAccord Difference
Partnering with a debt collection agency for late stage debt recovery provides a number of advantages, including improving debt recovery rates, reducing the workload for lenders, offering access to specialized resources, and providing flexibility and customization. Every business is different, just like every customer’s situation is different, but TrueAccord has proven for over a decade that our digital-first, omnichannel approach drives improvements in liquidation rates by engaging consumers with the right message, through the right channel, at the right time.
At TrueAccord, our mission to help organizations recover more (from happier consumers) is comprehensive and tailored to each business’s specific goals and individual customer expectations. Since 2013, we have provided win-win solutions between businesses and consumers in debt. By using our patented machine learning engine, HeartBeat, we create a personalized journey for each consumer and keep optimizing for the ideal message, outreach time, and communication cadence to elevate performance.